Keeping an eye on your blood sugar at home is a really important part of staying healthy, especially if you have diabetes. It might seem like a lot to handle, but with the right tools and a bit of planning, it’s totally doable. This article will walk you through how to monitor blood sugar at home effectively, so you can feel more in control and make good choices for your health.
Key Takeaways
- Regularly checking your blood sugar helps you understand your body better.
- There are cool gadgets and apps that make monitoring easier than ever.
- Making a plan for checking your blood sugar that fits your life is key.
- Using technology can really help you keep track of your numbers and stay on schedule.
- What you eat, how much you move, and even your stress levels all play a part in your blood sugar.
Understanding Blood Sugar Monitoring

The Importance of Regular Monitoring
Keeping an eye on your blood sugar isn’t just something doctors tell you to do; it’s a big part of staying healthy, especially if you’re dealing with diabetes. Regular monitoring helps you see how your body reacts to different foods, activities, and even stress. It gives you the information you need to make smart choices every day. Think of it like getting real-time feedback on your health. Without this feedback, it’s tough to know if what you’re doing is actually working.
Monitoring your blood sugar isn’t about perfection; it’s about understanding your body’s unique patterns and making informed adjustments to your daily routine. It’s a tool for self-awareness and proactive health management, not a judgment of your efforts.
Recognizing High and Low Blood Sugar Levels
Knowing what high and low blood sugar feels like is super important. It helps you act fast when something’s off. Here’s a quick rundown of common signs:
- High Blood Sugar (Hyperglycemia):
- Low Blood Sugar (Hypoglycemia):
If you notice these signs, it’s a good idea to check your blood sugar right away to confirm what’s going on and take appropriate action.
Interpreting Your Blood Glucose Readings
Once you’ve got your blood glucose numbers, what do they even mean? It’s not just about the number itself, but also when you took the reading. Here are some general ranges, but remember, your doctor will give you personalized targets:
| Time of Reading | Normal Range (mg/dL) | Prediabetes Range (mg/dL) | Diabetes Range (mg/dL) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fasting | Less than 100 | 100-125 | 126 or higher |
| 2 hours after meal | Less than 140 | 140-199 | 200 or higher |
Understanding these numbers helps you and your healthcare team figure out if your current plan is working or if you need to make some changes. For example, if your blood glucose monitoring shows consistently high numbers after meals, it might mean adjusting your diet or medication. It’s all about using the data to guide your health journey.
Tools for Effective Blood Sugar Monitoring
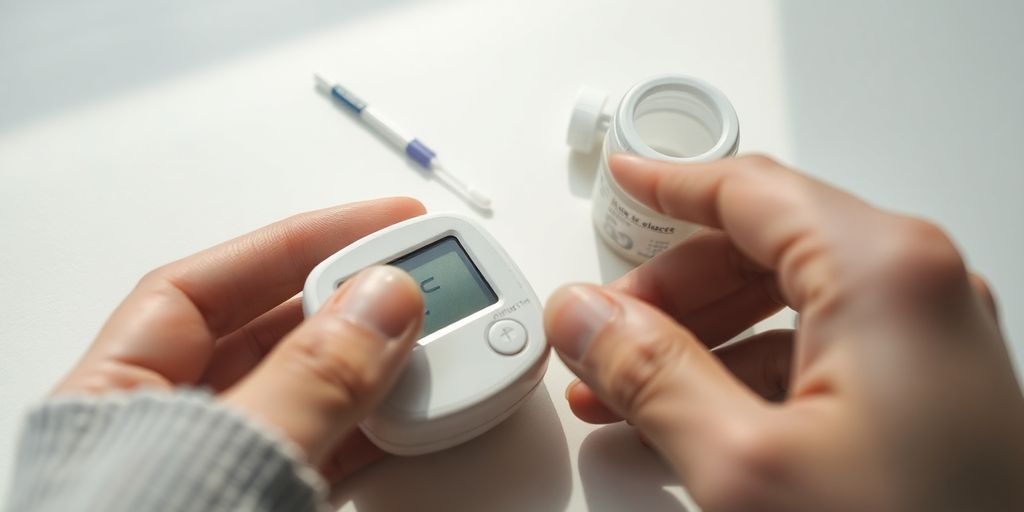
Utilizing Glucose Meters and Test Strips
When you’re trying to keep tabs on your blood sugar, the classic glucose meter and test strips are usually the first things people think of. They’re pretty straightforward: you prick your finger, put a tiny drop of blood on a test strip, and the meter gives you a reading. It’s a quick snapshot of your blood sugar at that exact moment. Getting accurate readings from your glucose meter is super important for making good decisions about your health. You gotta make sure your hands are clean, the strips aren’t expired, and you’re using the right amount of blood. It’s not rocket science, but little things can throw off the numbers.
These meters are generally reliable for spot checks, giving you a clear picture of your glucose levels before meals, after meals, or at specific times your doctor recommends. They’re a good starting point for anyone new to monitoring, and they’ve been around for ages because they work.
Here’s a quick rundown on getting the most out of your meter:
- Always check the expiration date on your test strips. Old strips can give you wonky results.
- Store your strips properly, usually in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight.
- Calibrate your meter if the instructions say to, or use control solutions to make sure it’s reading correctly.
- Don’t reuse lancets. Seriously, just don’t. They get dull and can hurt more.
Exploring Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs)
Now, if you want to get a bit more advanced, continuous glucose monitors, or CGMs, are where it’s at. These devices are a game-changer for a lot of people. Instead of pricking your finger multiple times a day, a CGM has a tiny sensor that you insert just under your skin, usually on your arm or belly. This sensor measures your glucose levels in the interstitial fluid, which is the fluid surrounding your cells. It sends readings to a receiver or your smartphone every few minutes, giving you a constant stream of data. It’s like having a live feed of your blood sugar. For example, the Stelo Glucose Biosensor offers 24/7 monitoring.
This constant data lets you see trends you’d totally miss with just a regular meter. You can see how different foods affect you, how exercise impacts your levels, and even how stress plays a role. It’s pretty eye-opening. Plus, many CGMs have alarms that can warn you if your sugar is going too high or too low, which is a huge relief for many.
Benefits of using a CGM:
- Real-time data, showing trends and patterns.
- Fewer finger pricks, which is a big win for comfort.
- Alerts for high or low glucose, helping prevent emergencies.
- Better understanding of how lifestyle choices affect blood sugar.
Leveraging Smartphone Apps for Tracking
Okay, so you’ve got your meter or your CGM, and you’re getting all this data. What do you do with it? That’s where smartphone apps come in. There are tons of apps out there designed to help you track your blood sugar, log your meals, record your exercise, and even connect with your healthcare team. Some apps can even sync directly with your CGM, pulling in all that real-time data automatically. It’s pretty slick.
Using an app can help you organize your information, spot patterns, and share your progress with your doctor. It’s way easier than keeping a paper logbook, and most apps have features that make it simple to see your average glucose, time in range, and other important metrics. Plus, many offer reminders for testing or taking medication, which is super helpful when life gets busy.
When picking an app, think about what you need:
- Does it connect with your specific meter or CGM?
- Can you log meals, exercise, and medication easily?
- Does it offer insights or reports that are easy to understand?
- Is it user-friendly? If it’s too complicated, you won’t use it.
- Does it have reminder features for testing or medication?
Developing a Personalized Monitoring Plan
Setting Realistic Blood Sugar Goals
When you’re trying to get a handle on your blood sugar, it’s super important to set goals that actually make sense for you. Don’t aim for perfection right out of the gate; that’s just going to stress you out. Your doctor or a diabetes educator can help you figure out what numbers are good for your specific situation. Everyone’s different, so what works for one person might not work for another. Think about your lifestyle, your other health stuff, and what you can realistically stick with every day.
It’s not about being perfect, it’s about being consistent. Small, steady changes are way more effective than trying to do too much too fast and then burning out.
Establishing a Consistent Testing Schedule
Once you have your goals, you need a plan for checking your blood sugar. A consistent schedule helps you see patterns and understand how different things affect your levels. It’s like keeping a diary for your blood sugar. Here are some common times to test:
- First thing in the morning, before you eat anything.
- Before meals.
- Two hours after meals.
- Before and after exercise.
- Before bed.
Your healthcare team can help you figure out the best times for you. Remember, the idea is to gather enough data to make smart choices, not to turn every day into a blood sugar test marathon.
Adjusting Your Plan Based on Lifestyle
Life happens, right? Your blood sugar monitoring plan shouldn’t be set in stone. It needs to be flexible enough to change with your life. Maybe you’re going on vacation, or you start a new exercise routine, or your stress levels go up. All these things can mess with your blood sugar. This is where personalized care plans come in handy. You might need to:
- Test more often during sick days or when you’re feeling stressed.
- Adjust your testing times if your work schedule changes.
- Talk to your doctor about medication adjustments if your diet or activity levels shift significantly.
It’s all about being aware and making small tweaks as needed. Your plan is a living document, not a rigid rulebook.
Integrating Technology for Better Management
Choosing the Right Diabetes Management App
Picking the right app for managing your diabetes can feel like a big decision, but it’s really about finding something that fits your daily routine. You want an app that does more than just log numbers; it should help you understand what those numbers mean. A good app will offer features that simplify tracking and provide insights into your blood sugar trends. Think about what you need most: maybe it’s carb counting, or perhaps you just want a simple way to keep all your health info in one spot. Make sure the app gets regular updates too, so you don’t run into annoying bugs or outdated features. User-friendliness is key; if it’s too complicated, you probably won’t stick with it.
Connecting Devices for Seamless Data Flow
Modern technology makes it super easy to get all your health data in one place. Many apps can connect directly with your glucose meter or even a continuous glucose monitor (CGM). This means less manual entry for you and a more complete picture of your blood sugar patterns. It’s pretty cool how your devices can talk to each other, saving you time and making sure your records are accurate. This kind of digital diabetes management can really make a difference.
When your devices are connected, the data flows automatically, creating a detailed log of your blood sugar levels without you having to lift a finger. This automation helps you and your doctor see trends more clearly, making it easier to adjust your plan as needed.
Utilizing Reminders and Alerts for Testing
Life gets busy, and it’s easy to forget to check your blood sugar. That’s where app reminders come in handy. Most diabetes management apps let you set up custom alerts for testing times, medication doses, or even after meals or exercise. This helps you stay on track without constantly thinking about it. It’s like having a personal assistant for your health.
- Set reminders for pre-meal checks.
- Schedule alerts for post-meal readings.
- Get notifications for medication times.
- Receive prompts for testing after physical activity.
Lifestyle Factors Influencing Blood Sugar
Impact of Diet on Glucose Levels
What you eat plays a huge role in how your blood sugar behaves. It’s not just about avoiding sugary stuff, though that’s a big part of it. Different foods break down into glucose at different rates, and that affects how quickly your blood sugar goes up after a meal. Think about it: a piece of white bread will hit your system way faster than a bowl of lentils. Understanding how various foods affect your glucose is key to keeping things steady.
Here are some general guidelines for managing blood sugar through diet:
- Prioritize whole, unprocessed foods: This means lots of vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and lean proteins. These foods tend to have more fiber, which slows down sugar absorption.
- Watch your portion sizes: Even healthy foods can cause a spike if you eat too much. It’s all about balance.
- Be mindful of carbohydrates: Carbs are the main source of glucose. Learn which carbs are complex (better for you) and which are simple (can cause quick spikes).
- Include healthy fats and proteins: These can help slow down digestion and prevent rapid blood sugar increases.
It’s not about strict deprivation, but rather making smart, consistent choices. Small changes over time can lead to big improvements in your blood sugar control. Learning to read food labels and understanding the glycemic index of foods can be really helpful tools in your dietary journey.
The Role of Physical Activity in Blood Sugar Control
Moving your body is like magic for blood sugar. When you exercise, your muscles use glucose for energy, which helps lower the amount of sugar in your bloodstream. It also makes your body more sensitive to insulin, meaning the insulin you do produce works more effectively. This is a win-win situation.
Even moderate activity can make a difference. You don’t have to become a marathon runner overnight. Just getting up and moving throughout the day can help. Consider these options:
- Brisk walking: Aim for at least 30 minutes most days of the week.
- Strength training: Building muscle helps your body use glucose more efficiently.
- Dancing or cycling: Find activities you enjoy so you’re more likely to stick with them.
- Taking the stairs: Small changes add up.
Regular physical activity can significantly improve HbA1c levels over time, which is a long-term measure of blood sugar control.
Managing Stress for Stable Blood Sugar
Stress is a sneaky one. When you’re stressed, your body releases hormones like cortisol, which can actually raise your blood sugar levels. It’s a survival mechanism, but in our modern lives, chronic stress can mess with your glucose control. It’s not always easy to eliminate stress, but finding ways to manage it is super important.
Here are some ways to tackle stress and help your blood sugar stay more stable:
- Practice relaxation techniques: Things like deep breathing, meditation, or yoga can calm your nervous system.
- Get enough sleep: Lack of sleep can increase stress hormones and make insulin resistance worse.
- Engage in hobbies: Doing things you enjoy can be a great stress reliever.
- Connect with others: Social support can reduce feelings of isolation and stress.
- Set realistic expectations: Don’t try to do everything at once. Prioritize and take things one step at a time.
Building Your Diabetes Support Network
Managing blood sugar isn’t something you have to do all by yourself. In fact, having a good support system can make a huge difference in how well you handle things day-to-day. Think of it like building a team around you, all working towards the same goal: your health. It’s about getting help from the pros, connecting with others who get it, and even bringing your loved ones into the loop.
Collaborating with Healthcare Professionals
Your healthcare team is your first line of defense and your main source of reliable information. They’re the ones who can give you the right advice, adjust your treatment, and help you understand what’s going on with your body. Regular check-ups and open communication with these folks are super important for staying on track.
Here’s who you might want on your team:
- Primary Care Doctor: Your go-to for overall health and referrals.
- Endocrinologist: A specialist in hormones and metabolism, perfect for diabetes management.
- Diabetes Educator: They teach you the ropes, from diet to medication.
- Dietitian: Helps you figure out what to eat to keep your blood sugar steady.
- Pharmacist: Can answer questions about your meds and how they work.
- Mental Health Professional: For managing stress and emotional well-being.
It’s easy to feel like you’re bothering your doctor with every little question, but that’s what they’re there for. Don’t hesitate to ask about anything that’s on your mind regarding your blood sugar or overall health. They can’t help if they don’t know what’s going on.
Finding Support Groups and Communities
Sometimes, talking to people who are going through the exact same thing as you can be incredibly helpful. Support groups, whether online or in person, offer a unique kind of understanding and encouragement. It’s a place where you can share your struggles and successes without feeling judged.
- Local Meetings: Check with your doctor’s office or local hospitals for groups in your area.
- Online Forums: Websites and social media groups dedicated to diabetes can connect you with people worldwide.
- Community Events: Sometimes, health organizations host events where you can meet others and learn more.
Diabetes support groups can be a real game-changer for your mental and emotional health. Knowing you’re not alone in this journey can make a huge difference.
Engaging Family and Friends in Your Journey
Your loved ones can be a huge source of support, but they might not always know how to help. It’s up to you to tell them what you need. This isn’t about them policing your food choices or nagging you; it’s about them understanding your challenges and being there for you.
- Educate Them: Share information about diabetes so they understand what you’re dealing with.
- Communicate Your Needs: Let them know how they can best support you, whether it’s by joining you for walks or just listening.
- Involve Them in Healthy Habits: Cook healthy meals together or plan active outings as a family.
- Set Boundaries: Make it clear what kind of support is helpful and what isn’t.
Wrapping Things Up
So, we’ve talked a lot about keeping an eye on your blood sugar. It might seem like a lot to take in, but honestly, it’s about making small changes that add up. Think of it this way: every time you check your sugar, you’re just getting a little more information about your body. It’s not a test you can fail, just data. Knowing what’s going on helps you make better choices, and that’s what really matters for feeling good and staying healthy in the long run. You got this!
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is it important to check my blood sugar regularly?
Keeping an eye on your blood sugar helps you understand how your body reacts to food, exercise, and stress. This knowledge is key to making smart choices that keep your blood sugar in a healthy range, which can prevent serious health problems down the road.
What’s the difference between a regular glucose meter and a Continuous Glucose Monitor (CGM)?
A glucose meter is a small device that checks your blood sugar using a tiny drop of blood, usually from your fingertip. A CGM, or Continuous Glucose Monitor, is a small sensor you wear on your skin that automatically checks your blood sugar levels all day and night, sending the info to your phone or another device. CGMs give you a more complete picture of your sugar levels over time.
How can I tell if my blood sugar is too high or too low?
When your blood sugar is too high, you might feel very thirsty, need to pee a lot, or feel tired. If it’s too low, you might feel shaky, sweaty, confused, or dizzy. Knowing these signs helps you act fast to get your levels back to normal.
Can smartphone apps really help me manage my blood sugar?
Many smartphone apps can help you track your blood sugar readings, log your meals, and even record your exercise. Some can connect directly to your glucose meter or CGM, making it super easy to keep all your health information in one place and share it with your doctor.
How do my daily habits, like eating and exercise, affect my blood sugar?
Eating balanced meals with plenty of vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein can help keep your blood sugar steady. Regular physical activity also helps your body use insulin better, which lowers blood sugar. And don’t forget stress! High stress can raise blood sugar, so finding ways to relax is important.
Who should be part of my team to help me manage my blood sugar?
Your healthcare team, including your doctor, a diabetes educator, and a dietitian, can give you expert advice and support. Joining a support group lets you connect with others who understand what you’re going through. And don’t forget your family and friends; their understanding and encouragement can make a big difference.






